Here you will find everything you need to know about ropes and cables. What is the difference between a wire, strand and a rope? Which rope constructions do exist? What is meant by lay directions? What is the effect of stretching? What materials are available? What is a coated rope and what is it required for? These and other questions we, from Carl Stahl Technocables would like to answer here.
Our expertise in the field of fine ropes
Do you need help choosing the right rope for your application?
Strands are made of single high tensile wires. These are placed helically around an insert * (heart wire) in the steel cable factory. This is the basic model for the further rope prodution.
A wire rope is produced by twisting strands. In addition to a strand (-WSC), a fiber interlayer (-FC) can also be used as the insert.
In special cases, a rope (-IWRC) can also be used as an insert.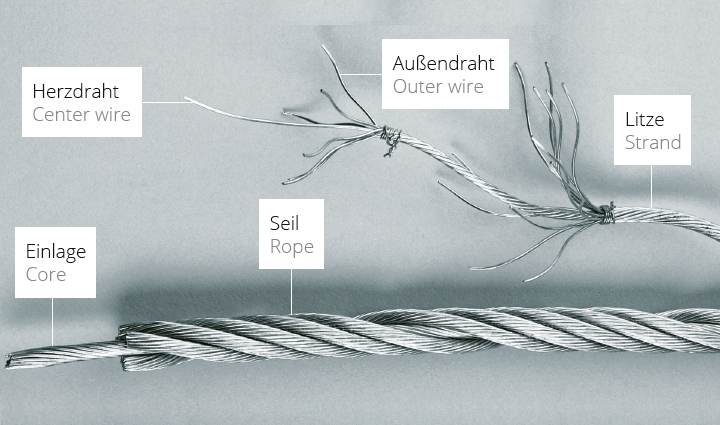
Steel ropes or wire ropes are designated as follows:
(Number of strands) x (number of wires per strand)
Example: 6x7-WSC corresponds to a rope consisting of 6 strands of 7 wires including a heart strand.
The lay direction indicates the direction in which the outer wires (outer strands) of the strand (cable) are laid around the center wire (core strand).

Strand in S-lay – left hand lay direction of wires.

Strands in Z-lay (lright hand ay direction of wires).

Steel cables with right hand ordinary lay (sZ).

Steel cables with left hand ordinary lay (zS).

Steel cable with right hand langs lay (zZ).

Steel cable with left hand langs lay (sS).
“S-lay” means: the outer wires (outer strands) are laid in left direction around the center wire (core strand).
“Z-lay” means: the outer wires (outer strands) are laid in right direction around the center wire (core strand).
Furthermore, a distinction is made between ordinary/regular lay and langs in the stranding (see figure). As standard, Carl Stahl Technocables delivers the steel cables in right hand ordinary lay (sZ).
Strand constructions: 1x7, 1x12, 1x19
Applications: Suspension and tensioning systems, Control cables, Inlay for belts
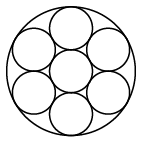
Strand 1x7
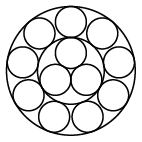
Strand 1x12
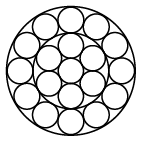
Strand 1x19
More information about our strands
strands / wire ropes made of stainless steel
strands / wire ropes made of galvanized steel
strands / wire ropes made of tungsten
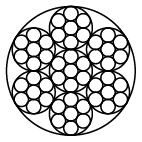
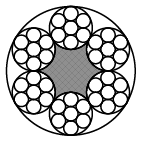
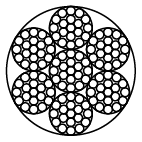
Rope constructions: 6x7-WSC, 6x7-FC, 6x19-WSC, 6x19-FC, 8x7+1x19, 8x19+7x7, 6x37-FC
In our own rope factory we can also individually produce ropes in other constructions.
Material: stainless steel, galvanized steel, tungsten, conductive ropes e-rope: stainless steel and copper, steel and copper
Applications: Control cables, Suspension and tensioning systems, Bowden cables
Wire rope 6x7-WSC
Wire rope 6x7-FC
Wire rope 6x19-WSC
Wire rope 6x19-FC
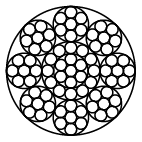
Wire rope 8x7+1x19

Stahlseil 8x19+7x7
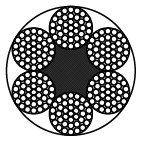
Stahlseil 6x37-FC
More information about our ropes
wire ropes made of stainless steel
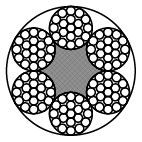
Coated rope constructions: 6x7-WSC, 6x7-FC, 6x19-WSC, 6x19-FC, 8x7+1x19, 8x19+7x7
Applications: Control cables, Suspension and tensioning systems, Bowden cables

Wire rope 6x7-WSC coated

Wire rope 6x7-FC coated
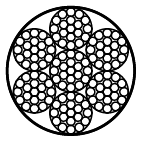
Wire rope 6x19-WSC coated
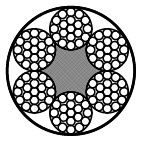
Wire rope 6x19-FC coated
Wire rope 8x7+1x19 coated
Wire rope 8x19+7x7 coated
wire ropes made of stainless steel
strands / wire ropes made of stainless steel
strands / wire ropes made of galvanized steel
strands / wire ropes made of tungsten
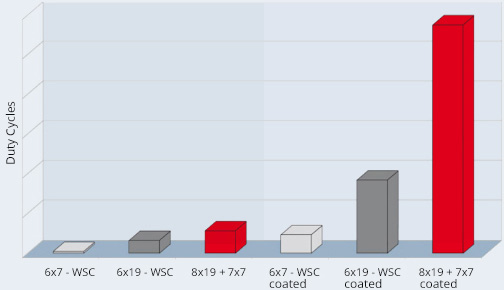
For example, in the case of cable systems that run over pulleys, we recommend using coated cables in order to achieve a high bending cycle and a long service life. With higher bending cycles a longer service life could be achieved.
Carl Stahl Technocables uses polyamide as the standard coating material. Polyamide is an optimum cable coating, distinguished by its high wear resistance and high bending cycle capability. A further advantage of the coated cables: The coating protects the rope from dirt.
We recommend PA12 if the cable runs over a pulley or if flexibility is the main priority. This is our standard coating material.
Furthermore, the coating keeps the manufacturing lubricant within the rope. This film of oil functions as a lubricant between the individual wires and strands, thereby reducing wear on the cable.
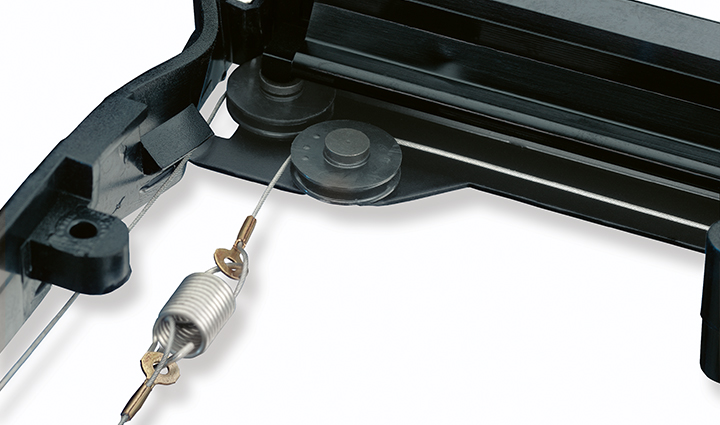

Are high temperatures or good sliding properties required of your steel wire rope? Then we use special materials for coating of the steel wire rope. For example, we recommend FEP/PTFE for temperatures of between -190°C and + 205° C.
We can also offer PA6.
Depending on the application, the appropriate coating material is used. Don’t you know which wire rope coating is the right for your rope application? - We're glad to help you finding the right material. Contact us directly
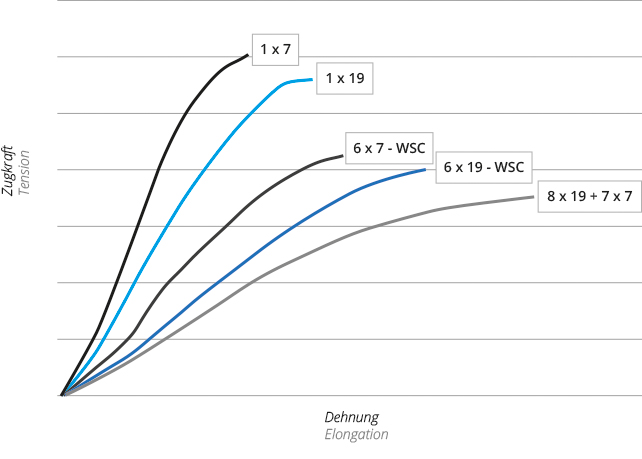
Two different kinds of elongation can be distinguished:
1. Constructional elongation
After the manufacturing process of the ropes and strands, small gaps remain between each wire within the strand and between each strand in the rope. When the rope is tensioned, the wires and the strand move closer to each other, and reach their optimum position. A result of this process is, that the rope elongates to a certain extent. This constructional elongation is not the same in every rope construction. It depends on lay, lay length, rope construction and other factors.
2. Material elongation
This elongation concerns the material that the single wires are made of. It occurs, when the wire is tensioned. The material elongation is proportional to the applied load. Under normal circumstances the rope will almost regain its original length as soon as the load is removed.
Contact us directly for your individual cable solution
We can recommend suitable steel cables for your purposes.
With Carl Stahl TECHNOCABLES, you will find the right steel cable to meet your requirements.
Contact us directly for your individual cable solution. We can recommend suitable steel cables for your purposes. The service life of strands and cables depends on many factors:
Roll diameter
Groove shape
Deflection 90°-180°
Constant load
Dynamic load
Acceleration
Diagonal pull
Test speed
Stroke length
Testing until cable breakage
Test stop when the number of test cycles has been reached
Roll storage
Simple bending/counter-bending
The diverse properties and possibilities of wire ropes and strands are attracting more and more attention when it comes to implementing mechanical applications flexibly and safely. The result is high-quality solutions for a wide range of applications, in a wide variety of industries. The possible applications of wire ropes are almost endless. Wire ropes with larger diameters up to 8.00 mm are used in mechanical engineering or in the sun protection sector. Fine wire ropes with smaller diameters from 0.09 mm are used in the medical, furniture or lighting industries, among others. Optical aspects also often play a role.
The selection of the right wire rope for the respective application is of great importance. This is done according to various criteria, which are selected on the basis of the respective area of application. Properties and conditions such as tensile strength, environment, corrosion resistance, form, function, surface and structure are taken into account.
Standard wire ropes and strands are made of galvanized steel, or stainless steel. Stainless steel ropes, for example, offer very high corrosion protection, are solid and have a very long service life. Wire ropes made of galvanized wire, are in many cases the most economical option and offer sufficient corrosion protection for various applications.
Carl Stahl Technocables GmbH is your competent partner from the initial consultation, through the development of technical specifications, to the manufacture of assembled ropes, Bowden cables, wire ropes and strands. We supply our products to a wide variety of industries and markets worldwide.
Ropes made of stainless steel are rustproof. They score high on durability due to low abrasion, are solid and have low ductility. Stainless steel ropes offer high tensile strength for mechanical applications and are temperature resistant.
Stainless steel is a corrosion-resistant alloy of iron, chromium-nickel and other elements, containing not less than 10.5% chromium, and its specific ratios vary depending on the alloy. The higher the chromium content in stainless steel, the higher the corrosion resistance. There are different types of stainless steel cables. We mainly use AISI 316 / 1.4401 or AISI 304 / 1.4301. The most common stainless steel is 1.4401. We also offer other stainless steels on request.
1.4401 is a stainless austenitic chromium-nickel-molybdenum steel. Special properties are e.g. good corrosion resistance.
1.4301 is the standard material for austenitic chromium-nickel steels. It is characterized above all by its good workability and also has a high corrosion resistance. AISI 304 / 1.4301, for example, has about 10 percent more tensile strength than equivalent materials.
Although the differences between stainless steel specifications are small, they affect their effectiveness in various applications. For example, the additional molybdenum content in 316 stainless steel helps make it even more corrosion resistant than 304.
AISI 304 / 1.4301 is widely used in medical applications due to its strength, malleability, precision in manufacturing and reliability. In addition, it is recyclable, heat resistant.
Stainless steel wire rope is the right choice for applications where the rope needs to be protected from corrosion. Applications that are likely to be used outdoors, underwater or in an area where the wire rope would be exposed to the elements. In particular, it is highly resistant to corrosion by acids and bases.
In the case of steel cables made of galvanized steel, the steel has undergone a galvanizing process called hot-dip galvanizing or HDP. HDP is the process of immersing the steel in molten zinc, which forms a coated zinc layer around the steel that protects the material from corrosion. While it is not as corrosion resistant as stainless steel cable, it is sufficient for an outdoor application in some cases.
The low cost-to-benefit ratio of galvanized steel wire rope makes this the preferred material for many mechanical applications intended for indoor use such as hanging heavy signage or suspending, lifting or balancing large objects.
An overview of the advantages of tungsten wire ropes and strands can be found here:
Which wire rope is best suited for many cycles in an application with bending cycles depends on many factors. One of these is how flexible a rope is, which is related to the construction, as well as the material from which a rope is made. Tungsten ropes have special material properties, are more flexible and have a longer service life than conventional stainless steel ropes. This can reduce maintenance and repair costs or increase safety for a certain service life.
The standard wires for steel wire strands and cables are made of galvanised steel or stainless steel 1.4401/ AISI 316. Galvanised wire offers sufficient corrosion protection for many areas of use. If the steel wire cables and strands are to be used in highly corrosive media, we recommend stainless steels.
In order to meet your special cable requirements, we also produce cables using other materials. In addition to the standard materials, stainless steel and galvanised steel special materials are also used, such as the following for example:
Brass | Copper | Titanium | Tantalum | Monel | Inconel | Hastelloy
For the jewellery industry Carl Stahl TECHNOCABLES produces cables and strands in:
Gold | silver | platinum | palladium
We can supply you with fine ropes or the finest strands with diameters in the tenth of a millimetre range from 0.09 mm. As a rope manufacturer with many years of experience, we produce the thinnest stainless steel ropes or galvanised steel ropes in various constructions. Fine ropes for the most precise applications are further processed in our assembly department.
The diameter of the deflection pulley / guide pulley is decisive for the service life of the rope that is deflected or guided by the pulley. A deflection pulley that is too small can considerably shorten the service life of the rope. The rope construction is also very important for the service life. The more wires the rope has with the same diameter, the more flexible it is, which can lead to an increase in service life. In order to achieve a long service life with extremely small deflection pulleys / guide pulleys, the design and quality of the deflection pulley (shape and material) and the selection of a suitable rope are crucial. The rope material also has a decisive influence on the service life of the rope. The service life of tungsten ropes can be up to 5 times longer than that of stainless steel ropes (material 1.4401/AISI316).
When using a small / miniature pulley, the bending stress can be extremely high. As a result, the service life of the wire rope suffers or even the pull-off force of the ready-to-install assembly is insufficient. To enable the use of the smallest miniature pulleys, it is necessary to select a rope with high bending fatigue strength. This rope has a long service life despite high bending stress on a pulley.
To achieve the longest service life in your application, our highly flexible tungsten wire ropes are best suited.
The service life under bending fatigue loading from pulleys / guide pulleys depends on many individual factors. The tensile load on the rope and the dynamic load have a major influence. The service life of the rope can also be increased by selecting a different rope construction and a different rope material. Due to the high strength of our tungsten ropes, a significantly longer service life is possible compared to conventional stainless steel ropes.
The use of a smaller pulley subjects the rope to greater bending stress. This stronger bending can lead to a reduction in the service life of the rope. In order to be able to use a smaller pulley with a comparable service life, the alternating bending strength of the rope must be higher.
This flexural fatigue strength can be increased by using a different rope construction or a different rope material.